LoRaWAN, or Long Range Wide Area Network, has become an essential pillar in the world of the Internet of Things (IoT). Faced with the growing challenges of optimizing performance and managing infrastructures, companies are looking for technological solutions capable of connecting multiple devices reliably, securely and cost-effectively. LoRaWAN, with its extended range and low energy consumption, is emerging as a strategic choice for the digital transformation of intelligent buildings. Discover how this innovation is transforming our daily lives and propelling businesses towards a more connected, high-performance future.
Introduction to LoRaWAN
Definition
LoRaWAN, or Low Power Long Range Network, is a wireless communication protocol based on LoRa(Long Range) modulation. It is designed to connect objects over long distances, while minimizing energy consumption. LoRaWAN is ideal for transmitting low-bandwidth data over several kilometers. This capability makes it particularly well suited to IoT sensors, especially for building and infrastructure management. In particular, LoRaWAN is used to connect sensors in complex environments where other technologies such as Wi-Fi fail due to long distances or physical obstacles. It also extends the battery life of connected devices.
The origins of LoRaWAN: a collaborative initiative
LoRaWAN is based on an emerging technology, LoRa, developed in 2009 by Cycleo, a French company. Subsequently, the acquisition of Cycleo by Semtech Corporation led to the standardization of this technology for IoT communications.
The real breakthrough came with the formation of the LoRa Alliance in 2015, a non-profit organization whose aim is to promote and standardize the use of LoRaWAN technology for IoT networks. It brings together over 500 members, including companies from various sectors such as telecommunications, energy, industry, technology and utilities. The main role of the LoRa Alliance is to define and maintain open LoRaWAN communication standards, ensuringinteroperability between equipment and networks worldwide.
This standardization is crucial to enable global adoption of the technology and ensure that LoRaWAN sensors and gateways can communicate effectively, regardless of the vendor or infrastructure used. In addition, the alliance fosters collaboration between its members to accelerate innovation and deployment of IoT applications in diverse sectors such as smart cities, agriculture, industry 4.0, and critical infrastructure.
What are the differences between LoRa and LoRaWAN?
It's important not to confuse LoRa with LoRaWAN. LoRa is the radio modulation used to transmit data over long distances. LoRaWAN, on the other hand, is the network protocol that uses this modulation to manage communications between sensors, gateways and application servers. LoRa is the "transmission technique", while LoRaWAN is the "network architecture" that makes large-scale transmission possible.
If we use a metaphor to simplify, we can see LoRa as the equivalent of radio waves, i.e. the technology used to send messages. LoRaWAN, on the other hand, would be like a postal service: it deals with the management of these messages, how they are transported, delivered and managed across a network. Thus, LoRa is essential for long-range, low-power communication, while LoRaWAN enables the creation of a structured, secure and intelligently managed network for large-scale IoT applications.
| LoRA | LoRaWAN |
|---|---|
| Modulation technology used to transmit data wirelessly over long distances. | Network protocol that defines how these devices connect, and how data is sent and received between devices, gateways and the backend. |
| Covers only the physical part (radio modulation layer) of the communication. | Takes care of network management, security and communication between sensors and servers. |
| Used in IoT devices and sensors to send low-power radio signals. | Defines rules for managing communication on a large-scale IoT network. |

How does LoRaWAN work?
Robust network architecture
A key feature of LoRaWAN is its use of free frequency bands (ISM - Industrial, Scientific and Medical). These frequency bands vary from region to region:
- Asia: Different bands are used, such as 433 MHz and 920 MHz.
- Europe: LoRaWAN mainly uses the 868 MHz band.
- North America: The 915 MHz band is used.
Furthermore, LoRaWAN uses a star architecture, which means that all IoT devices or sensors communicate directly with gateways, without there being any direct communication between the devices themselves.
- Devices (IoT sensors): These are connected objects that measure data (temperature, power consumption, pressure, etc.) and transmit them to the nearest gateway via the LoRa protocol.
- LoRaWAN gateways: Gateways act as intermediaries between IoT sensors and the central server. They receive radio signals (in LoRa) from the sensors and transmit them to the network server via the Internet, a cellular connection or another communications infrastructure (e.g. Ethernet). Gateways can listen on several channels in parallel, enabling many devices to be managed at the same time.
- Network server (backend): This server plays a central role in managing the LoRaWAN network. It ensures correct data routing, verifies message integrity, manages connected devices, and ensures that data is secure.
- Application servers: Once sensor data has been processed by the network server, it is sent to the application server, which uses it for analysis, visualization, or to trigger specific actions. For example, in an energy management solution, building consumption data can be sent to a platform like EwattchCloud for analysis and energy optimization.
- Protocols: LoRaWAN defines the communication rules between sensors and servers, including security mechanisms (AES-128 encryption), connection management, and data rate adaptation (ADR - Adaptive Data Rate) to maximize transmission efficiency.
- Device classes: LoRaWAN offers three classes of device, depending on communication needs and energy consumption:
Class A: Devices transmit data only at irregular intervals and open reception windows immediately after transmission, optimizing energy savings.
Class B: These devices are synchronized to receive data at regular intervals, at the cost of slightly higher energy consumption.
Class C: These devices keep a receive window open at all times, ensuring near-real-time communication, but at the cost of higher energy consumption.
Comparison of LoRaWAN and other wireless technologies
| Features | LoRaWan | Wi-Fi | Bluetooth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Up to 15 km (rural), up to 2 km (urban) | Limited to a few dozen meters | Very limited range (10-100 m depending on version) |
| Energy consumption | Very low (sensors can last several years) | Relatively high (suitable for connected devices) | Very low but depends on application |
| Data rate | Low (a few kbps) | High (up to 1 Gbps with Wi-Fi 6) | Very low (up to 2 Mbps) |
| Infrastructure costs | Low (free ISM bands, few gateways) | Medium to high (requires routers and infrastructure) | Very low (integrated in most devices) |
| Scalability | Very high (can manage thousands of devices) | Limited by local network capacity | Limited to local networks (nearby devices) |
| Security | Integrated AES-128 encryption | Secure but depends on local network | Basic security, more suitable for simple connections |
| Typical use case | Large-scale monitoring, industrial surveillance | Home automation, offices, homes | Headsets, wearables, connections between devices |
LoRaWAN applied to IOT solutions
Why is LoRaWAN ideal for IOT sensors?
LoRaWAN offers many advantages for IOT projects, particularly in terms of range, energy consumption and infrastructure costs. Here are the main benefits of this technology:
- Security: LoRaWAN integrates two levels of encryption (network and application) to ensure that transmitted data is protected against interception and tampering. This level of security is essential for sensitive applications such as industrial surveillance or smart cities.
- Long range: LoRaWAN can cover vast geographical areas, with a range of up to 15 kilometers in rural areas and up to 2 kilometers in urban areas. This makes it an ideal solution for connecting sensors on large infrastructures such as farms, industrial buildings or smart cities.
- Low power consumption: The power consumption of LoRaWAN devices is optimized to extend the life of battery-powered sensors. Class A devices, for example, can operate for several years without requiring a battery change, which is crucial for sensors installed in hard-to-reach locations.
- Low cost: Unlike cellular networks or some Wi-Fi solutions, LoRaWAN operates on free frequency bands (ISM), eliminating the need for subscriptions or data usage costs. What's more, LoRaWAN gateways can be deployed by the company itself, enabling the creation of private networks without recurring communication costs.
- Scalability: LoRaWAN can handle thousands of devices with a minimum number of gateways, enabling large-scale IoT networks to be set up without costly infrastructure. This makes it ideal for use cases such as power grid surveillance, environmental monitoring and smart building management.
Practical applications of LoRaWAN for BMS
Building Management Systems (BMS) are a strategic issue for companies wishing to optimize their infrastructures, reduce costs and improve operational efficiency. Here are a few concrete examples of LoRaWAN applications that can transform your building management and help you maximize performance while reducing costs:
- Energy consumption monitoring: LoRaWAN sensors can be used to monitor the energy consumption (electricity, gas, water) of a building or facility in real time. This data can be used to identify anomalies, optimize consumption and reduce energy costs.
- HVAC equipment management: Sensors can collect data on temperature, humidity or the operation of heating and air-conditioning equipment, enabling real-time adaptation of comfort conditions while avoiding energy wastage.
- Predictive maintenance: by continuously monitoring the condition of equipment (compressors, heating systems, etc.), IoT sensors can alert managers when a device shows signs of malfunction, even before a breakdown occurs. This makes it possible to plan maintenance interventions and avoid costly shutdowns.
- Monitoring sensitive environments: In environments such as server rooms or laboratories, LoRaWAN sensors can monitor critical parameters such as temperature, humidity or vibration, guaranteeing the safety and smooth running of installations.
EWATTCH solutions based on LoRaWAN
Ewattch offers a range of innovative IoT solutions, based on LoRaWAN technology, to help companies control their energy consumption and optimize the management of their infrastructures.

Squid Pro: An advanced energy sub-metering solution
Specially designed to identify where energy is consumed within industrial or tertiary infrastructures, this IOT sensor enables energy consumption to be segmented by zone or equipment, making it easier to identify sources of waste.
- Save energy
- Average ROI in less than 12 months
ambiance sensors: Intelligent comfort and energy management
Sensors in the Ambiance range measure temperature, humidity, air quality and other environmental parameters in real time.
- Save on HVAC energy costs
- Improve occupant comfort

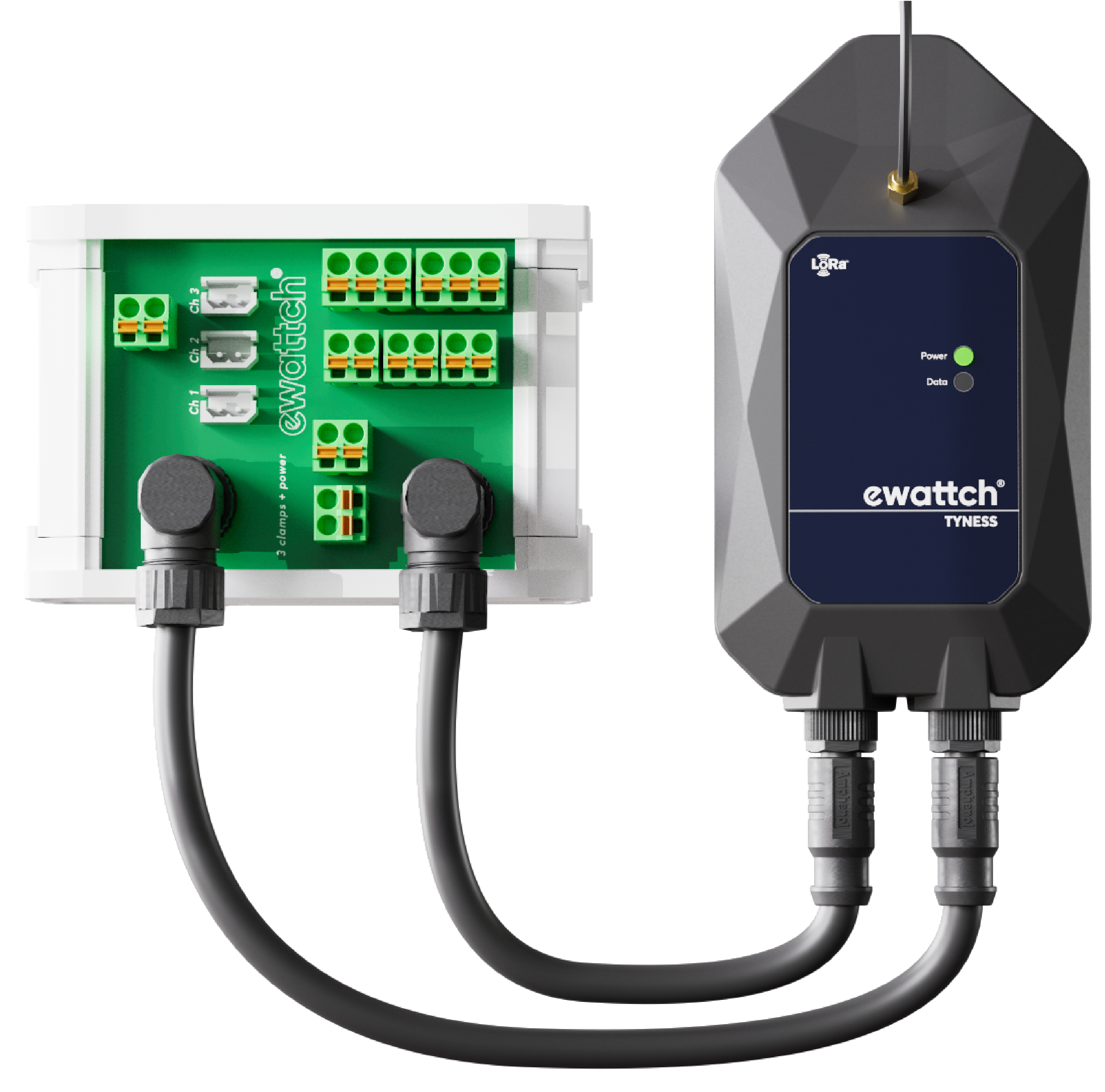
Tyness: Predictive maintenance and monitoring of industrial equipment
Tyness is a sensor dedicated to monitoring industrial equipment. It enables real-time monitoring of the performance of machines such as compressors, chillers or production systems, in order to optimize their use and prevent breakdowns.
- Reduce maintenance costs
- Detect anomalies on your equipment
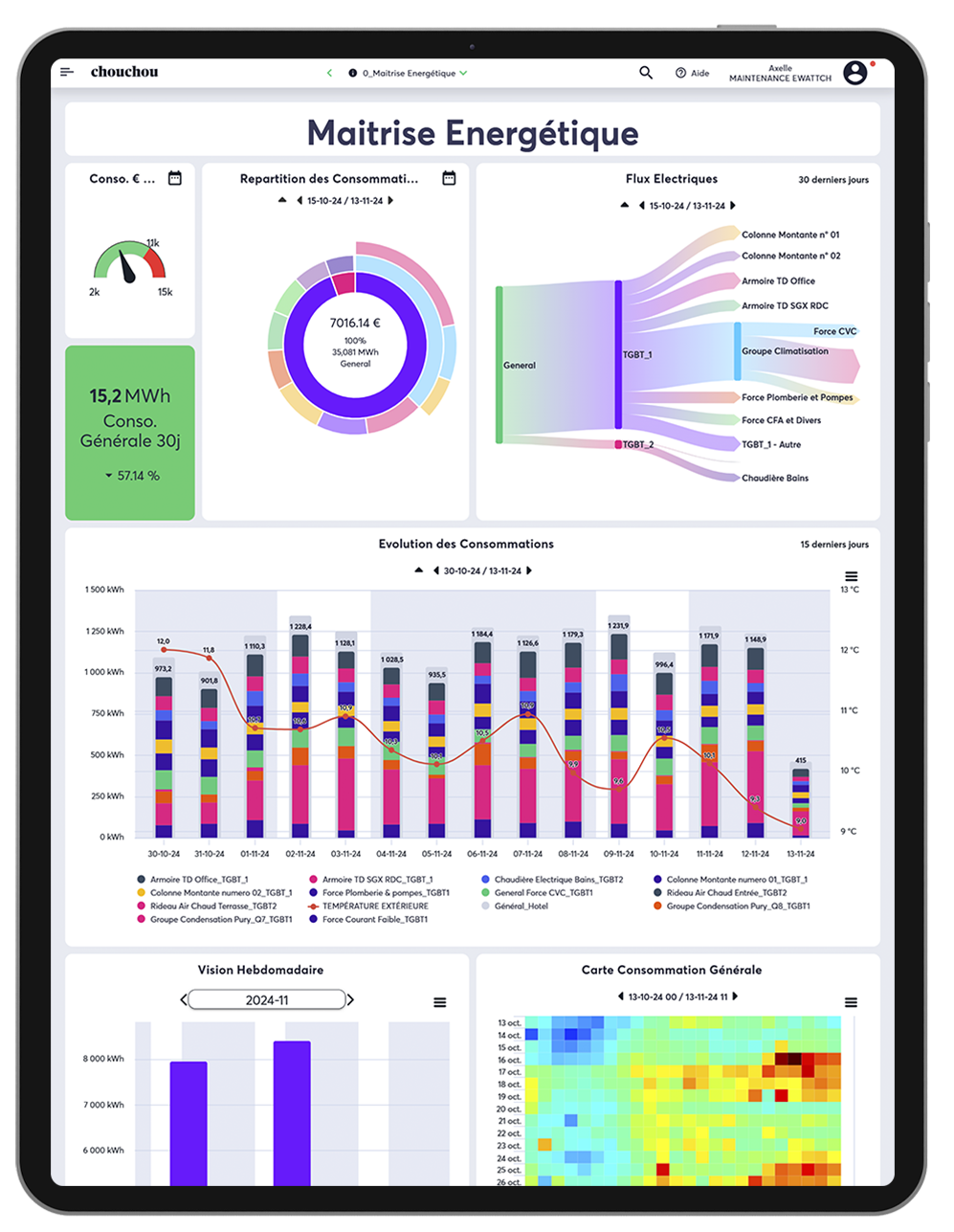
EwattchCloud: Centralized management platform
EwattchCloud is the centralized platform for real-time visualization of all data collected by LoRaWAN sensors deployed throughout a company. This solution offers customizable monitoring tools, automatic alerts and detailed reports, facilitating the energy and technical management of infrastructures.
- Analyze data in real time on EwattchCloud.
- Monitor your sites at a glance, regardless of the number of installations