Solution Bâtiments
Smart Building, energy-saving and compliance solutions
Companies in the service sector face these two major challenges,
which Ewattch® provides effective solutions.

BACS decree compatible

Reduce energy bills by up to 40%.

Improved occupant comfort

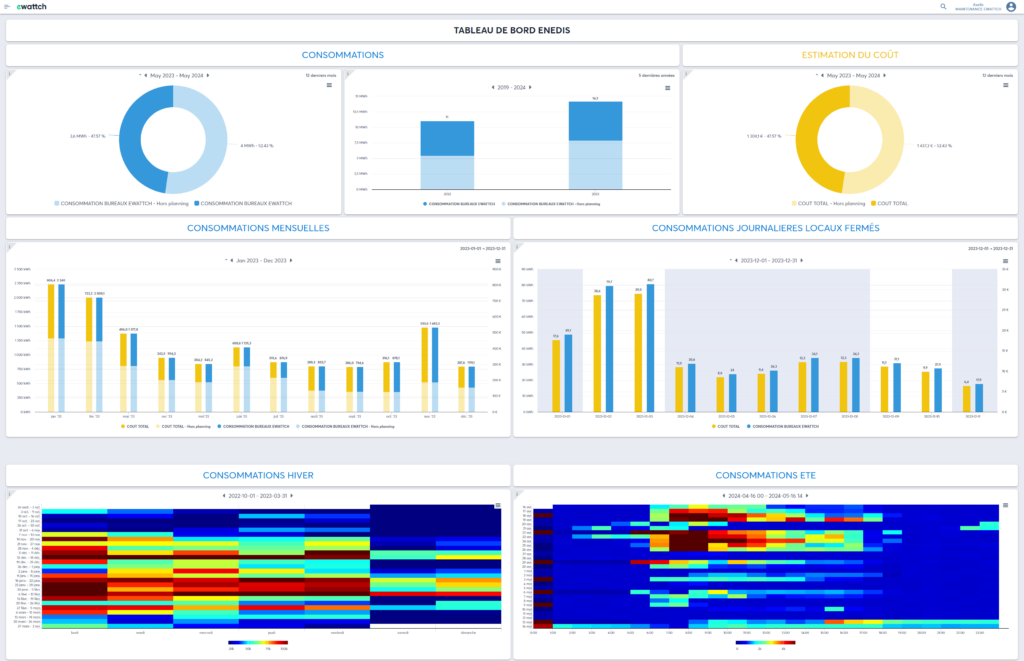
Monitoring consumption and implementing action plans

Benefits
Digitizing your building, the ultimate solution
for energy optimization
Ewattch stands out as a key player in the commercial sector, offering a complete range of intelligent, integrated solutions that meet today's business challenges, including carbon footprint reduction, corporate environmental responsibility and regulatory compliance.
A compliant building
Our Smart Building solution, based on IoT sensors and an IoT platform, helps commercial businesses to comply effectively with current regulations, including the requirements of the tertiary and BACS decrees, while anticipating future legal obligations.

Rapid return on investment
Achieve average energy savings of 30% in the first few months, with ROI in less than three months.


Start
your
project today
An Ewattch expert assists you in connecting your general meter to the EwattchCloud IoT platform.
Your smart building project comes to life quickly and with minimal initial investment.


Flexible software
& easy to use
Would you like to extend the capabilities of your intelligent building even further? Would you like to benefit from new functionalities or work with other companies? The Ewattch solution is designed to be compatible with a wide range of applications and partners.
EwattchCloud
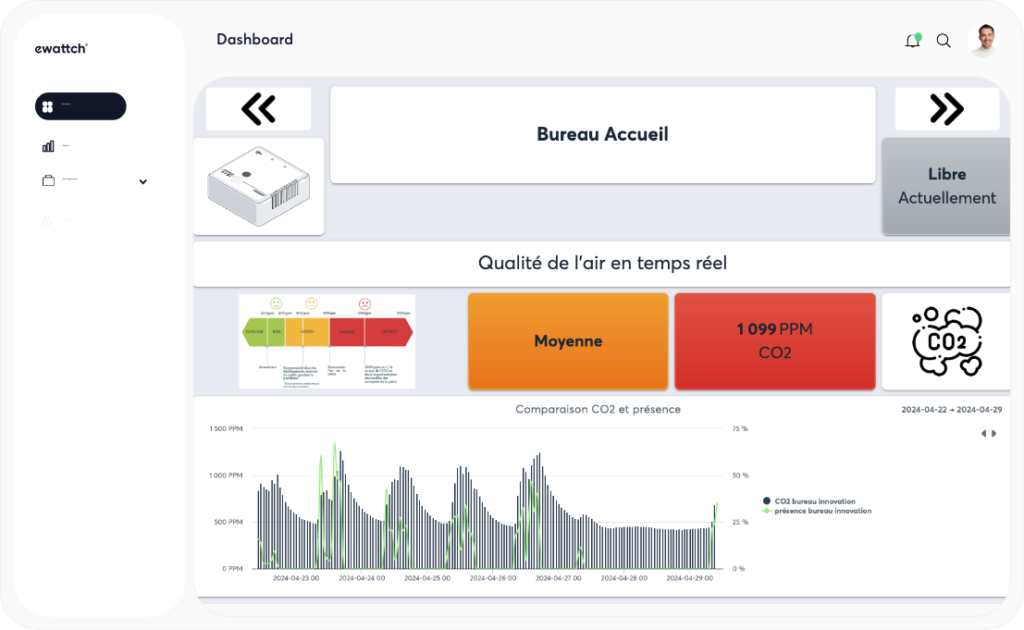
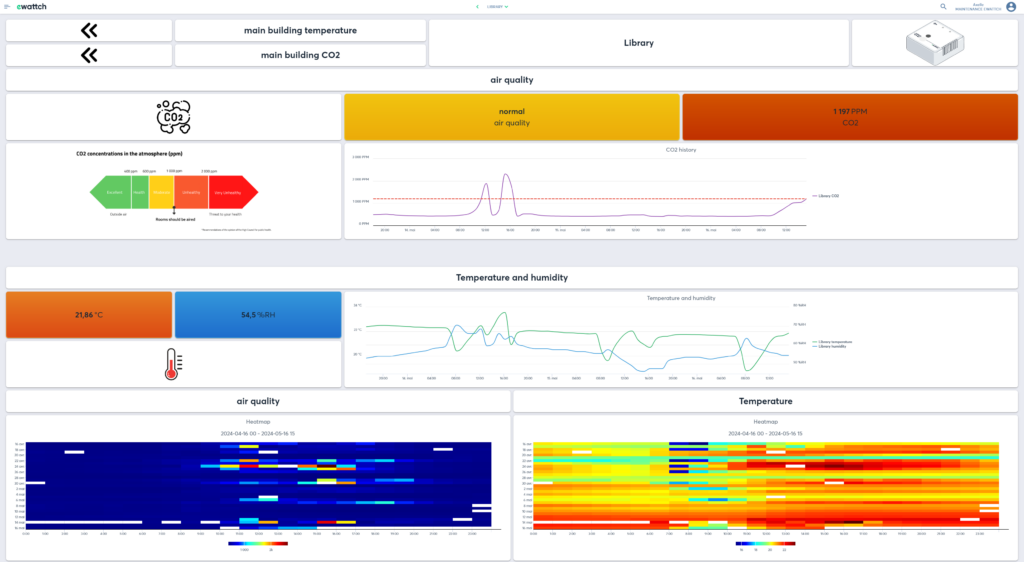
Air quality
In addition to reducing energy consumption, the Ewattch solution optimizes occupant comfort and well-being, thanks to sensors for CO2, temperature, presence and other environmental indicators.

Multi-site system
Consolidate the energy management of your various sites on a single IoT platform. So you can prioritize your actions and optimize your investments efficiently.
Go further with the Ewattch network of complementary applications
Connected to our IOT platform, they enable you to manage your buildings in greater depth.
Technology
The intelligent tool for making informed decisions and prioritizing initiatives
From now on, your decisions will be based on your actual energy data, not on estimates.

Enedis meter
Connection of the general meter to the Ewattch IoT platform via a simple online form, without the need to install additional IoT sensors.

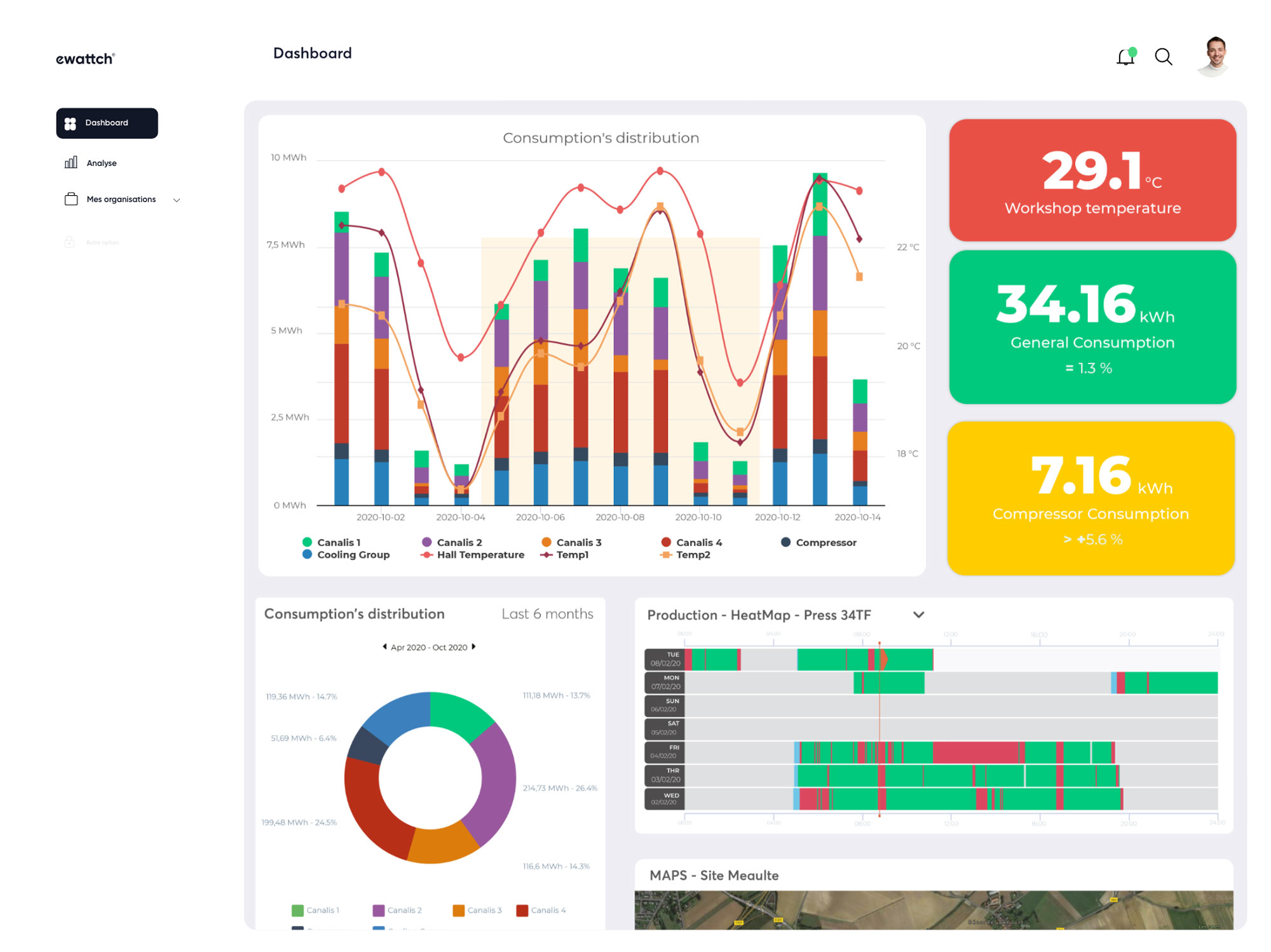
Squid
Detailed analysis of electricity consumption by zone and by use, precise detection of anomalies, strategic prioritization of actions, and calculation of return on investment (ROI).

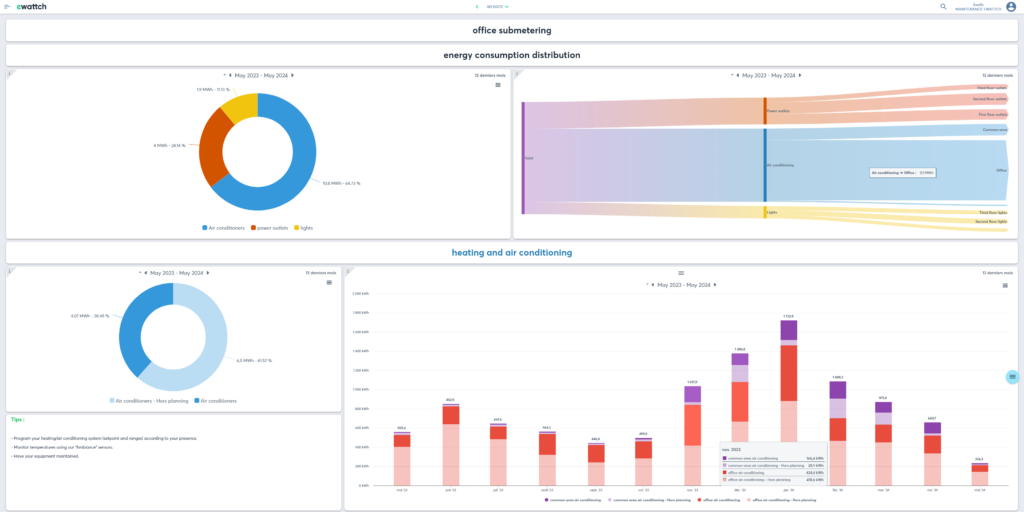
Ambiance
Optimization of heating and air conditioning to improve thermal comfort for occupants and energy efficiency in buildings.

Would you like to
evaluate your savings potential?
Method
Energy efficiency
within your reach
With Ewattch, you can optimize the energy efficiency of your commercial buildings in a targeted, cost-effective way, without the need for over-equipment.




Commissioning
Accessible, efficient technology
for Smart Buildings
After years of research and innovation, Ewattch unveils its exclusive, high-performance technology: ScanToCloud. This technological breakthrough considerably simplifies the deployment of energy management solutions by optimizing the connection between sensors and the IoT platform.

Simplified deployment,
independently or with
Ewattch support
ScanToCloud simplifies product integration with the EwattchCloud IoT platform, offering fast connection and facilitating instant energy monitoring.
Testimonials
They have reduced their
bill and their carbon footprint.
Find out how Ewattch supports its customers to help them meet their challenges.
FAQ
FAQ - Everything you need to know about Smart Building
What is a Smart Building?
A Smart Building is a structure equipped with automated and connected systems to manage andoptimize building performance. These technologies, based on sensors and cloud platforms, collect and analyze data in real time to improve occupant comfort, safety, energy efficiency and building maintenance.
How does a Smart Building work?
A Smart Building works by integrating IoT (Internet of Things) sensors, building management systems (BMS) and energy management solutions. The data collected is sent to a cloud platform, where it is analyzed. These analyses help to automate and optimize various aspects of the building, such as temperature, lighting, ventilation and security, while reducing energy costs.
How does smart building comply with the tertiary sector decree and the BACS decree?
The BACS decree requires commercial buildings equipped with heating, ventilation or air-conditioning systems to install automation and control systems to optimize their energy consumption. This obligation initially applies to buildings with a rated output of over 290 kW, with a deadline of January 1, 2025. From January 1, 2027, the obligation will be extended to all commercial buildings with a rated output of over 70 kW. The decree aims to improve the energy efficiency of buildings by ensuring intelligent energy management.
At the same time, the tertiary sector decree requires these same buildings, with a surface area of over 1,000 m², to progressively reduce their energy consumption, with targets of 40% reduction by 2030, 50% by 2040, and 60% by 2050.
The Smart Building is the perfect response to these decrees, incorporating advanced technologies that go beyond minimum requirements. By digitizing technical management systems, it amplifies their effects, using cutting-edge technologies to furtheroptimize energy use and reduce costs. In this way, a Smart Building not only complies with decree obligations in terms of control and automation, but also optimizes these processes via the Internet of Things (IoT), the cloud, and artificial intelligence.
What's the difference between smart building and BMS?
Building Management Systems (BMS) and Smart Building are two closely related concepts, but they differ in scope, technology and objectives.
The BMS is a system for supervising and managing a building's technical installations, such as heating, ventilation, air conditioning, lighting and security. It centralizes the commands and controls of these systems for easier administration, enabling more efficient management of technical infrastructures.
Smart Building goes beyond BMS by integrating advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), data analysis and real-time connectivity. The aim is to optimize not only technical systems, but also the occupant experience, resource management, and interaction between the building and its external environment.
What role does the IOT play in Smart Building?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is at the heart of the transformation of buildings into Smart Buildings. The idea is to connect a large number of devices (sensors, cameras, thermostats, etc.) to the building's network. LoRa and LoRaWAN technologies are essential to this process. With their extended range, they enable efficient data transmission even in complex environments.
IOT technologies collect valuable data, which is then analyzed. This information is used to intelligently manage the building. Buildings equipped with IoT solutions can proactively respond to occupants' needs. They also adapt in real time to environmental conditions, improving efficiency, productivity and comfort.
In short, the IOT is the engine that transforms a traditional building into a smart building.
Why transform your building into a smart building?
Transforming a building into a smart building offers a number of significant advantages.
- Energy efficiency and cost reduction: By integrating IoT sensors, buildings can monitor their energy consumption in real time. This monitoring enables heating, ventilation and lighting systems to be optimized according to occupancy and actual conditions. Intelligent energy consumption translates into a significant reduction in operating costs, a major challenge for any company seeking to maximize profitability.
- Productivity and performance: thanks to equipment automation and predictive maintenance, smart buildings can anticipate and prevent breakdowns. This reduces downtime, improves plant reliability and cuts repair costs. What's more, by ensuring optimum comfort for occupants, these buildings create a more pleasant working environment, promoting employee productivity and well-being.
- Security and surveillance: Connected systems provide real-time monitoring, ensuring better management of operational risks. Sensors and cameras can detect anomalies, prevent incidents and ensure rapid response in the event of an emergency. In addition, regulatory compliance is simplified, as Smart Buildings can integrate technologies that meet legal security requirements. This proactive monitoring reduces the risk of accidents, theft or non-compliance, protecting corporate assets and ensuring a safe environment for occupants.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): By optimizing the use of energy resources and reducing emissions, smart buildings contribute to the goals of sustainability and environmental responsibility. With these installations, companies meet the growing expectations of consumers and investors, while improving their brand image.
What are the main use cases for data collection and analysis in a Smart Building?
A Smart Building can optimize various technical aspects by collecting and analyzing data. Here are a few use cases:
- Ventilation: optimized for occupancy rate and air quality.
- Temperature: precise temperature control at specific points in the building for optimum comfort.
- Energy production / consumption: Real-time monitoring and performance adjustment.
- Leak detection: System monitoring to detect and warn of leaks.
- Humidity: humidity monitoring to prevent mold and ensure air quality.
- Air quality: Monitoring of CO2 levels and other pollutants to adjust ventilation and maintain good air quality.
- Occupancy rate: to manage space and optimize building use.
- Equipment status: Continuous monitoring of equipment status (elevators, HVAC systems, etc.) to plan maintenance.
- Entry and exit detection: Control entry and exit flows to reinforce security and manage access.
- Brightness level: adjusts lighting according to natural light and time slots.
Is a smart building profitable?
Yes, the digital transformation of a building represents a long-term strategic investment on several levels:
- Reduced operating costs: Thanks to intelligent energy management, connected buildings optimize their consumption. This reduces waste and lowers energy bills. By automatically adjusting systems such as heating, air conditioning and lighting according to actual needs, a Smart Building can achieve substantial savings over the long term.
- Predictive maintenance and reduced breakdowns: The Smart Building integrates predictive maintenance technologies, enabling problems to be detected and resolved before they become critical. This approach reduces unplanned downtime and the costs associated with emergency repairs. By avoiding costly breakdowns and extending equipment life, building profitability is enhanced.
- Real estate enhancement: Smart Buildings increase the value of real estate assets. A building equipped with smart technologies is perceived as more modern, more efficient and more sustainable. This attracts not only potential tenants and buyers, but also investors. What's more, an energy-efficient building can benefit from premiums on real estate markets, boosting its attractiveness and long-term profitability.
- Compliance and tax benefits: Finally, by integrating technologies that comply with environmental and energy standards, Smart Buildings can benefit from tax benefits or subsidies. What's more, they are better prepared to comply with future regulations, avoiding additional costs associated with upgrades or penalties.
What types of buildings can be smart?
Any type of building can be transformed into a Smart Building, including offices, shops, municipal establishments, industries, hotels and restaurants, residences, cultural buildings, hospitals and care centers, etc.
What are the safety benefits of a smart building?
Smart buildings use advanced connected technologies that offer multiple safety benefits. These include:
- Real-time monitoring: Connected systems enable continuous, real-time monitoring of the entire building, quickly detecting any anomalies.
- Reduced operational risks: Thanks to IoT integration, the risks of incidents, such as breakdowns or failures of critical systems, are reduced through early detection and real-time alerts.
- Regulatory compliance: Smart Buildings facilitate compliance with current safety standards, by integrating technologies that meet legal requirements.
These combined benefits create a safer environment for building occupants and assets.








